Neural networks let microscopists see more
Researchers develop a method to overcome the limitations of microscopes
Fluorescence microscopy has become an indispensable tool to answer fundamental questions in the biomedical sciences. It visualizes the position of fluorescently labeled cellular building blocks in biological tissues and organisms. In living samples, dynamic processes can be imaged over the course of many hours, enabling researchers to investigate how cells form tissues and organs during embryonic development.
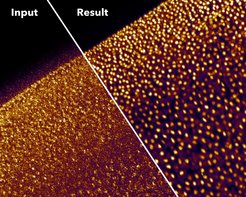
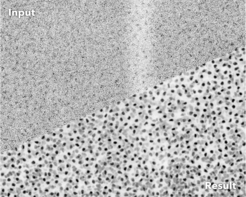
However, the quality of the obtained images strongly depends on the amount of light used during acquisition. Light levels leading to high-quality images can, unfortunately, cause undesired side effects. These side effects, known as phototoxicity, lead to changes in cellular behavior and can even be lethal for cells. Additionally, some organisms react with muscle flinching to even moderate amounts of light, also leading to unusable data. In order to avoid this “ultimate sunburn”, researchers have to limit the total amount of light used during imaging, which results in low-quality images that are hard to analyze.
An interdisciplinary group of researchers at the CSBD and MPI-CBG in Dresden, have now developed a method to get high-quality images despite using up to 60 times less light. The novel approach – CARE – is a self-learning Content-Aware image REstoration software based on artificial neural networks. The scientists reasoned that, although one cannot acquire a long movie of high-quality images without running into the phototoxicity trap, it would be possible to obtain pairs of image snapshots: one in low-light quality and the other one with sufficient light to generate clean images. These pairs of snapshots are used to train CARE networks that later help to make the “hidden” content in even very noisy images visible. In their study, recently published in Nature Methods, the researchers show that CARE can be successfully applied to many different microscopes, experiments, and organisms.
Break-through technology
Martin Weigert, first author and Myers lab member, says: “One of the main applications of our method will be to enable the observation of cell or tissue dynamics under highly challenging conditions by improving the quality of the acquired images.” Former Myers group member and co-author, Loïc Royer, who recently started his own research group at the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub in San Francisco, adds, “Imaging living organisms often requires compromises. With CARE, biologists won’t need to make such drastic compromises anymore. Our method makes previously impossible imaging experiments possible.”
“CARE is a prime example for the type of break-through technology that a truly interdisciplinary campus like ours here in Dresden-Johannstadt can produce. Computer scientists, physicists, biologists, and chemists from the CSBD, the MPI-CBG, and DRESDEN-concept institutions collaborated closely. Everyone brought their special expertise to make this fundamental advance!”, says Florian Jug, who was a key driver behind the work. He concludes, “CARE is now opening windows through which we can better observe the biological processes that govern life. We are excited to see what creative minds around the world will do with CARE.”